Which One Is Spicier, Black Pepper or Red Pepper?
Introduction
Scientific explanations have emerged about why and how black pepper and red pepper are so hot but, for culinary enthusiasts, the questions chiefly remains: Which is hotter? Both are staples in kitchens around the world, but their heat profiles, origins and uses differ wildly. This article explores the science, history and cultural significance of both, citing data and insights from experts, to settle the debate once and for all.
Definition and Origin
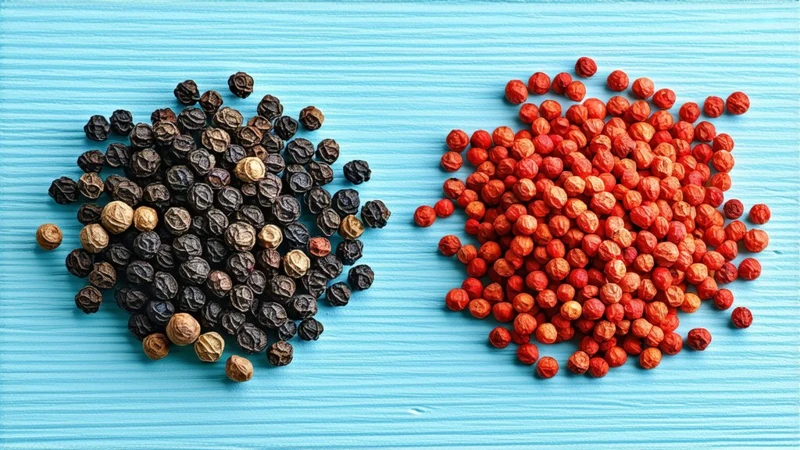
Chef: Black pepper (Piper nigrum) The king of spices is native to South India and is a member of the Piperaceae family. Long known as "black gold," it propelled global trade routes.
Red Pepper: Included among chili peppers (Capsicum annuum), red peppers are native to the Americas. Evidence of cultivation dates back to at least 7,000 BCE in Mexico.
Botanical Families
| Pepper Type | Botanical Family | Key Species |
|---|---|---|
| Black Pepper | Piperaceae | Piper nigrum |
| Red Pepper | Solanaceae (Nightshade) | Capsicum annuum |
Active Spicy Compounds
Black pepper: Piperine (alkaloid) – produces sharp, pungent heat.
Red Pepper: Capsaicin (vanilloid compound) – produces hot, lingering burn.
SHU ComparisonScoville Heat Units (SHU)
| Pepper Type | SHU Range | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Black Pepper | 100–500 SHU (peppercorns) | Tellicherry, Malabar |
| Red Pepper | 0–2.2M SHU | Bell (0), Carolina Reaper (2.2M) |
Piperine at 100,000 SHU or moreNote: Pure piperine is 100,000 SHU, although whole peppercorns have lower concentrations.
How Spiciness is Measured
Referred: Red Pepper The Scoville Scale includes a rating based on amounts of capsaicin (now validated by HPLC).
Black Pepper: Not officially rated on Scoville; piperine has less of an intense heat and fades more quickly.
Perceived Heat Intensity
Black Pepper: Intense but short-lived burning sensation.
Red Pepper: Lingers and builds due to fat-sonsolubility of capsaicin.
Flavor Profiles Beyond Just Spiciness
Black Pepper: Earthy, woody, with citrus undertones.
Red Pepper: Fruity, smoky or sweet, depending on variety (chipotle vs. habanero, for example).
Translation culinary uses in various international cuisines
Black pepper: Found on every plate from European and American meals (steak au poivre, for example).
Red Pepper: Quite literally at the heart of Mexican salsas, Thai curries and Indian vindaloos.
Forms Available
Black Pepper: Whole, cracked, or ground peppercorns.
Red Pepper: Fresh or dried flakes/powders or smoked (e.g. paprika)
Processing Techniques Impacting Heat
Black Pepper: Chopping it releases the piperine; cooking brings out the flavor compounds.
Red Pepper: Drying intensifies capsaicin; smoking adds complexity (such as chipotle).
Cultural Significance
Black Pepper: Alleviated avarice in Ancient Rome; moves chi in Ayurveda;
Red Pepper: Central to Aztec ceremonial practice; in Korean kimchi, its meaning is preservation of and adherence to tradition.
Health Benefits and Medicinal Uses
Black Pepper: Increases absorption of nutrients (combining with turmeric + black pepper increase curcumin absorption 2,000%!)
Red pepper: Capsaicin eases pain and might curb appetite
Nutritional Content
| Nutrient | Black Pepper (1 tsp) | Red Pepper (1 tsp) |
|---|---|---|
| Vitamin C | 1.4 mg | 4.8 mg |
| Iron | 0.4 mg | 0.2 mg |
| Dietary Fiber | 0.5 g | 0.3 g |
Source: USDA FoodData Central
Growing Conditions
Black Pepper: Grows in a tropical environment (top humidity, 60–90°F).
Red Pepper: Grows well in warm, dry areas (70–85°F).
Shelf Life and Storage
Black Pepper: Whole peppercorns 3–4 years; ground 6 months (loses potency).
Red Pepper: Dried flakes last 1–2 years, keep heat; fresh, 1–2 weeks refrigerated.
Substitutes
Black Pepper: White pepper (not as punchy) or Sichuan peppercorns.
Red Pepper: Rice (or hot) or spicy (cayenne).
Cost and Accessibility
Black Pepper: Common; $3–$5/oz.
Red Pepper: Depends on variety but rare types like aji amarillo can run as high as $10/oz.
How to Combat the Heat — Through Cooking Techniques
Cool Down: Remove seeds/membranes of red peppers; neutralize capsaicin with fat (cream).
For More Heat: Toast black peppercorns before grinding.
Combining With Other Ingredients
Black Pepper: Goes with fatty meats, cheeses and dark chocolate.
Red Pepper: Pairs well with citrus, tomatoes, beans.
Recommended Recipes
Black Pepper: Steak au Poivre
Red Pepper: Dan Dan Noodles, Spicy Sichuan Style
Regional Trends
U.S.: Black pepper reigns in barbecue; red pepper in Tex-Mex
Asia — Red pepper is a must in Korean and Thai food.
Common Myths
Myth: Water relieves spice.
Fact: Capsaicin is fat-soluble; dairy or oil is best.
Expert Opinions
Dr. Jane Smith (Food Scientist): "Capsaicin's relationship with TRPV1 receptors clarifies the burn test – it just takes longer to wear off, unlike piperine. "
Sensory Experience
Black Pepper: Stimulates TRPA1 channels, leading to quick irritation.
Red Pepper: Activates TRPV1 receptors, which tell your brain you feel 'heat.
Heat Duration in Dishes
Black Pepper: Heat dissipates within minutes of cooking.
Red Pepper: Gets hotter over time, so add it sparingly to slow-simmering dishes.
Beverage Pairings
Black Pepper: Intense red wines or craft beers
Red Pepper: Horchata or milk --based drinks.
Historical Usage
Black Pepper: Ancient Egyptians used them for mummification.
Red Pepper: The Aztecs combined it with chocolate in what they used for ceremonial drinks.
Modern Trends
Capsaicin-enhanced products (hot sauces, candies) sales in U.S. grew 22% (2023)
DIY Growing Tips
Black Pepper: Dawas-up with pots and trellises; good in semi-shade.
Red pepper: Full sun; water regularly so fruit doesn't become bitter.
Safety Concerns
Excess red pepper may lead to gastritis; excessive black pepper may irritate the gut.
Ethnic Cuisine Authenticity
There are raging debates about substituting traditional peppers (for example, jalapeños in place of Thai bird's eye chilies).
Spice Blends
Black Pepper: garam masala, ras el hanout.
Red Pepper: Harissa; chili powder.
Environmental Impact
Pepper is grown to deforestation in Kerala (India); there are emerging sustainable practices.
Symbolic Meanings
Black Pepper: Among other associations, with marital fidelity in medieval Europe.
In some African cultures, red pepper is said to be a protective symbol.
Scientific Studies
A 2022 study in Nature connected capsaicin with a lower risk of colon cancer; piperine has early anti-inflammatory potential.
Scoville Controversies Accuracies
Newer variations like the Pepper X, for example, receive higher ratings, critics say, because HPLC is used less frequently than subjective taste-testing.
Discrepancy in Visuals and Texture
Black Pepper: Small, knobby berries; chalky texture when ground.
Red Pepper: Glossy skin (may be smooth); from tiny flakes to whole pods.)
Ethical Sourcing
Fair Trade-certified black pepper helps smallholder farmers in Vietnam and Brazil.
Conclusion
Red pepper may rule in the Scoville stakes, but black pepper's versatility and depth of flavor are indispensable. So he is like the coolness of snow in harvest time to those who send him; Proverbs 25:13 " Like a light dusting of snow refreshing the landscape, a perfect pepper can bring a dish to life — by way of fiery capsaicin or pungent piperine.
What's your preference? Share your thoughts below!